Diversify Your Payment Options with Samsung Pay
Yasin Hosain
Engineer, Samsung Developer Program
This article demonstrates how to integrate Samsung Pay In-App Payments into your Android application, covering everything from account setup to release. Follow these steps to ensure a smooth integration process so you can start accepting payments with Samsung Pay quickly.
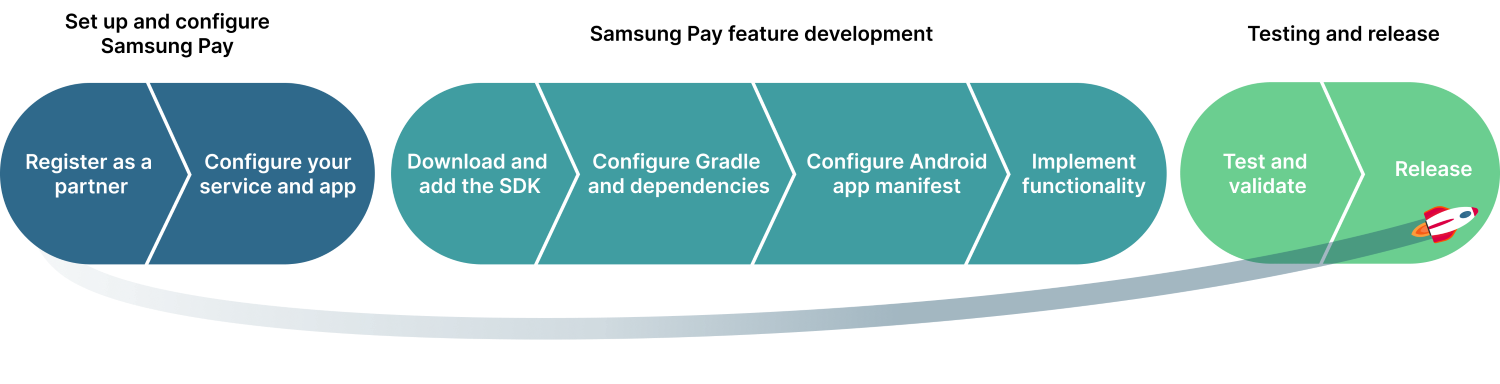
Figure 1: Steps of implementing Samsung Pay
Set up and configure Samsung Pay
Register as a partner
To begin accepting payments through Samsung Pay, first you need to register as a Samsung Pay partner and complete your Samsung Pay developer profile.
Visit the Samsung account website
Go to the Samsung account web site and do one of the following:
- If this is your first time on the site, click “Create Account” at the top right corner to create an account. For a smooth approval, use a business email (not personal) for registering your account.
- If you already have a Samsung account, simply log in.
Complete your developer profile
Follow these steps to enable your Samsung Pay developer account:
- Go to the Samsung Pay Developer portal and log in with a business account.
- Become a pay partner by creating a business account.
- Provide appropriate data which exactly matches your business and legal documents.
- Read the Terms and Conditions carefully and accept them.
- Submit your partnership request.
The approval process generally takes a few days. If you encounter any issues, please contact developer support for assistance.
Configure your service and app
While working with the Samsung Pay, you will encounter the terms “Service” and “App.” Let’s unpack them below.
Understanding Services and Apps
- Service: An interface to the Samsung Pay system that provides the payment facilities. The service talks with the Samsung Pay system and collaborates with the partner system and Payment Gateway for processing payments.
- App: An app works like a bridge between the service and the partner application. The app ensures the communication and security between the partner application and the service.
Create an In-App Payment Service
To create an in-app payment service, from the Samsung Pay partner portal, follow the steps below:
- Select Service management, under My projects in the top-right corner menu,
- In the Service management screen, click CREATE NEW SERVICE.
- Select the In-App Online Payment service type, then click SAVE AND NEXT.
- Enter the service information, attach a valid CSR file for secure payment, and then click SAVE AND NEXT.
- Fill in the required details to define your in-app service. If you have created one previously, you can also use it instead. Then click SAVE AND NEXT to advance to the next step.
- Define a tentative debug date by clicking GENERATE NEW DATE.
- Click ADD SAMSUNG ACCOUNT to add the Samsung accounts that will be used for testing purposes.
- Click DONE.

Figure 2: Creating an in-app payment service
This completes the creation of your service and links it with your application. Wait for it to be approved. The team will contact you promptly once your request has been processed. In case of any delays, feel free to reach out to 1:1 Support for assistance.
Samsung Pay feature development
Now that your partner account set up is complete, it's time to integrate Samsung Pay functionality into your Android application. Next we will integrate the Samsung Pay SDK and implement core payment features to enable seamless in-app transactions in your app.
Download and add the SDK
Go to the Downloads page in Samsung Pay and scroll down to the Android section to download the Samsung Pay SDK.
SDK components
The Samsung Pay SDK has the following components:
- Java Library (samsungpay_x.xx.xx.jar): Contains the classes and interfaces to integrate with the Samsung Pay.
- Sample Apps: Demonstrates the implementation of Samsung Pay APIs to simplify the process of building your own.
Add the SDK to your project
Create a folder called ‘libs’ if one does not already exist, and move the SDK .jar file into this folder.
/app
├── libs/
│ └── samsungpay_x.xx.xx.jar
├── src/main/
│ ├── kotlin/
│ ├── res/
│ └── AndroidManifest.xml
Configure Gradle and dependencies
- Update settings.gradle.kts
Add the ‘libs’ folder with the other repositories, if it is not there already.
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
flatDir { dirs 'libs' }
}
}
- Add the SDK Dependency in app/build.gradle.kts
Add the Samsung Pay SDK as a dependency for your application.
dependencies {
implementation(files("libs/samsungpay_x.xx.xx.jar"))
}
- Sync the Gradle to apply the changes.
Configure Android app manifest
Add the following configurations in your AndroidManifest.xml. This ensures the compatibility and proper functioning of your application.
- Add the
Element
<queries>
<package android:name="com.samsung.android.spay" />
</queries>
- Add Metadata
<meta-data
android:name="spay_sdk_api_level"
android:value="2.xx" /> <!-- Latest version is recommended] -->
Implement functionality
Now that the Samsung Pay SDK integration is complete, let us use this SDK to implement the complete functionality of the Samsung Pay SDK in your Android application. Here we will go through the complete flow of initiating a payment using the Samsung Pay SDK.
Check Samsung Pay availability
Initiating a payment starts by checking if Samsung Wallet is available for payment or not. Initialize the Samsung Pay service with your partner credentials, then verify if Samsung Pay is supported. If available, display the Samsung Pay button in your app.
val serviceId = "partner_service_id"
val bundle = Bundle()
bundle.putString(SamsungPay.PARTNER_SERVICE_TYPE, SamsungPay.ServiceType.INAPP_PAYMENT.toString())
val partnerInfo = PartnerInfo(serviceId, bundle)
val samsungPay = SamsungPay(context, partnerInfo)
samsungPay.getSamsungPayStatus(object : StatusListener {
override fun onSuccess(status: Int, bundle: Bundle) {
when (status) {
SamsungPay.SPAY_NOT_SUPPORTED -> samsungPayButton.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE)
SamsungPay.SPAY_NOT_READY -> {
samsungPayButton.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE)
val errorReason = bundle.getInt(SamsungPay.EXTRA_ERROR_REASON)
if (errorReason == SamsungPay.ERROR_SETUP_NOT_COMPLETED) samsungPay.activateSamsungPay()
else if (errorReason == SamsungPay.ERROR_SPAY_APP_NEED_TO_UPDATE) samsungPay.goToUpdatePage()
}
SamsungPay.SPAY_READY -> samsungPayButton.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE)
}
}
override fun onFail(errorCode: Int, bundle: Bundle) {
samsungPayButton.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE)
Log.d(TAG, "checkSamsungPayStatus onFail() : $errorCode")
}
})
Set up payment details and request the payment
After the availability check is completed, you need to set up the payment details such as merchant information, transaction information, order number, and so on, before requesting the payment. The following code snippets show how to accomplish this.
Make CustomSheet
Create a simple custom payment sheet with amounts and items for the transaction. This sheet will be displayed during the payment process. You can customize the sheet according to your requirements.
private fun makeUpCustomSheet(): CustomSheet {
val amountBoxControl =
AmountBoxControl(AMOUNT_CONTROL_ID, mBinding.currency.selectedItem.toString())
amountBoxControl.addItem(
PRODUCT_ITEM_ID,
mContext.getString(R.string.amount_control_name_item),
mDiscountedProductAmount,
""
)
amountBoxControl.addItem(
PRODUCT_TAX_ID,
mContext.getString(R.string.amount_control_name_tax),
mTaxAmount + mAddedBillingAmount,
""
)
amountBoxControl.addItem(
PRODUCT_SHIPPING_ID,
mContext.getString(R.string.amount_control_name_shipping),
mShippingAmount + mAddedShippingAmount,
""
)
amountBoxControl.setAmountTotal(totalAmount, amountFormat)
val sheetUpdatedListener = SheetUpdatedListener { controlId: String, sheet: CustomSheet ->
Log.d(TAG, "onResult control id : $controlId")
updateControlId(controlId, sheet)
}
val customSheet = CustomSheet()
customSheet.addControl(amountBoxControl)
return customSheet
}
Make CustomSheetPaymentInfo
Create payment information with merchant details, order number, and card brand preferences.
private fun makeTransactionDetailsWithSheet(): CustomSheetPaymentInfo {
// Get BrandList (supported card brands)
val brandList = getBrandList()
val customSheetPaymentInfo: CustomSheetPaymentInfo
val customSheetPaymentInfoBuilder = CustomSheetPaymentInfo.Builder()
customSheetPaymentInfoBuilder.setAddressInPaymentSheet(mRequestAddressOptions.requestAddressType)
customSheetPaymentInfo = customSheetPaymentInfoBuilder
.setMerchantId("your_merchant_id")
.setMerchantName("your_merchant_name")
.setOrderNumber("your_order_number")
.setAddressInPaymentSheet(CustomSheetPaymentInfo.AddressInPaymentSheet.DO_NOT_SHOW)
.setAllowedCardBrands(brandList)
.setCardHolderNameEnabled(mBinding.cardBrandControl.displayCardHolderName.isChecked)
.setCustomSheet(makeUpCustomSheet())
.build()
return customSheetPaymentInfo
}
Request the payment
Initiate the Samsung Pay payment process with transaction details and handle payment callbacks.
mPaymentManager.startInAppPayWithCustomSheet(
makeTransactionDetailsWithSheet(),
object : CustomSheetTransactionInfoListener{
override fun onCardInfoUpdated(
selectedCardInfo: CardInfo?,
sheet: CustomSheet?
) {
// Update your controls if needed based on business logic for card information update.
// updateSheet() call is mandatory pass the updated customsheet as parameter.
try {
paymentManager.updateSheet(customSheet)
} catch (e: java.lang.IllegalStateException) {
e.printStackTrace()
} catch (e: java.lang.NullPointerException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}
override fun onSuccess(
customSheetPaymentInfo: CustomSheetPaymentInfo?,
paymentCredential: String?,
extraPaymentData: Bundle?
) {
// Triggered upon successful payment, providing CustomSheetPaymentInfo and paymentCredential.
// For example, you can send the payment credential to your server for further processing with PG. Or you could send it directly to the PG as per business need.
sendPaymentDataToServer(paymentCredential)
}
override fun onFailure(errCode: Int, errorData: Bundle?) {
// Fired when the transaction fails, offering error codes and details.
Log.d(TAG, "onFailure() : $errCode")
showErrorDialog(errCode, errorData)
}
})
Testing and release
Test and validate
To ensure a seamless and reliable integration of Samsung Pay, thorough testing is essential. This process validates transaction performance and guarantees a positive user experience for making a robust business impact. Testing goes beyond error detection; it aims to comprehensively assess the quality and functionality of your Samsung Pay integration.
Release
After successful testing, the next step is to secure release version approval from Samsung through the Samsung Pay Developers portal. Once approved, your application can be launched, allowing you to monitor user satisfaction and optimize performance.
Conclusion
By integrating Samsung Pay In-App Payments, you’ve enabled secure, convenient transactions for Samsung Pay users. This implementation expands your payment options while providing a seamless checkout experience.
Additional Resources
For additional information on this topic, refer to the resources below.


