Measure Electrodermal Activity on Galaxy Watch
Objective
Create a health app for Galaxy Watch, operating on Wear OS powered by Samsung, utilizing Samsung Health Sensor SDK to obtain Electrodermal Activity (EDA) measurement results.
Overview
Samsung Health Sensor SDK provides tools for accessing and tracking health information stored in the health data repository. Its tracking service delivers both raw and processed sensor data, including accelerometer readings and body composition metrics, collected by the Samsung BioActive sensor. Electrocardiogram (ECG), bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), photoplethysmogram (PPG), heart rate, skin temperature, blood oxygen (SpO2), and sweat loss data can be measured. Furthermore, the Galaxy Watch8 introduces Electrodermal Activity tracking.
Electrodermal Activity (EDA) is a non-invasive physiological index that measures changes in skin conductance driven by sweat gland activity, reflecting the autonomic nervous system's response to both thermoregulation and psychological arousal.

See Samsung Health Sensor SDK documentation for detailed information.
Set up your environment
You will need the following:
- Galaxy Watch8 or newer
- Android Studio (latest version recommended)
- Java SE Development Kit (JDK) 17 or later
- Android API level 36 or later
Sample Code
Here is a sample code for you to start coding in this Code Lab. Download it and start your learning experience!
Electrodermal Activity Sample Code (159.8 KB)
Connect your Galaxy Watch with Android Studio
Watch the video below to connect to your Galaxy Watch. For detailed instructions, visit this guide: Connect Galaxy Watch with Android Studio
Turn on Developer Mode for Health Platform
Watch the video below to enable developer mode for Health Platform on your Galaxy Watch. For detailed instructions, visit this guide: Health Platform’s developer mode
Start your project
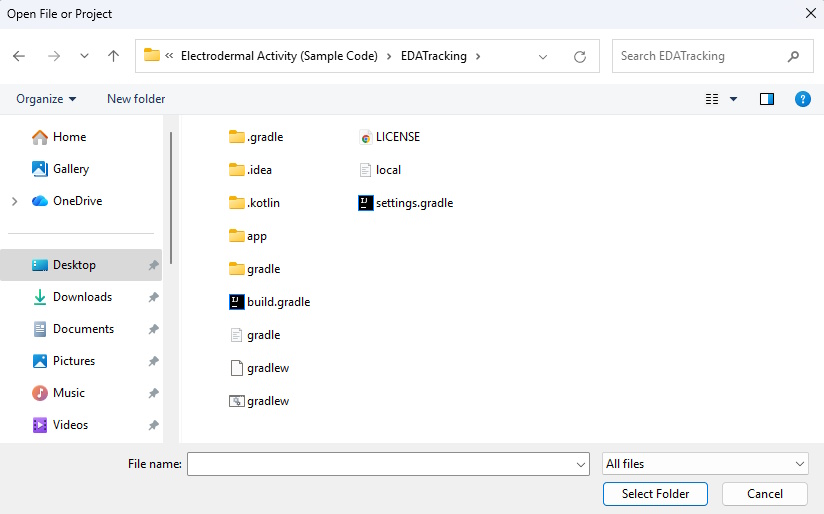
In Android Studio, click Open to open existing project.

Locate the downloaded Android project (EDATracking) from the directory and click Select Folder.
Request for health permission
The app utilizing Samsung Health Sensor SDK requires the appropriate permissions and the user’s consent to access the vital signs information. Different permissions are required depending on the HealthTrackerType you want to measure. While this Code Lab focuses solely on HealthTrackerType.EDA_CONTINUOUS tracker type, the READ_ADDITIONAL_HEALTH_DATA permission is also being used.
NoteIf the app’s target SDK version is Android 15 (API level 35) or lower, BODY_SENSORS permission is used.
Go to app > manifests > AndroidManifest.xml and ensure the required permissions are added:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BODY_SENSORS" />
<uses-permission android:name="com.samsung.android.hardware.sensormanager.permission.READ_ADDITIONAL_HEALTH_DATA" />
Next, the app needs to check if the user has already granted the permissions:
private fun isPermissionGranted() = ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(
applicationContext,
permission!!
) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED
If no permission is granted, request the necessary permissions.
Go to app > kotlin+java > com.samsung.health.sensorsdksample.edatracking > presentation > MainActivity.kt and navigate to the preparePermission() function. Complete the function to provide appropriate permissions based on the Android version:
/****************************************************************************
* [Practice 1] Request health permissions
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* Use the provided variable 'permission'.
* Replace 'null' with proper value based on Android version.
* If Android SDK version is higher or equal Android SDK 36 (BAKLAVA) use "com.samsung.android.hardware.sensormanager.permission.READ_ADDITIONAL_HEALTH_DATA" permission.
* Otherwise use "android.permission.BODY_SENSORS".
****************************************************************************/
fun preparePermission(): String? {
val permission = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// TODO: Replace 'null' with proper String value here
null
} else {
// TODO: Replace 'null' with proper String value here
null
}
return permission
}
The returned permission is used in the requestPermissions() function, which displays a pop-up asking for the user’s consent.
Initialize EDA tracker
Before starting the measurement, initialize the EDA tracker by creating a HealthTracker object.
Navigate to app > kotlin+java > com.samsung.health.sensorsdksample.edatracking > tracking > EDATrackingManager.kt and locate the obtainEDATracker() function.
Using the provided healthTrackingService object, create an instance of the HealthTracker class with the EDA_CONTINUOUS type and assign it to the edaTracker variable.
- Retrieve the
HealthTracker object using getHealthTracker().
- Use
HealthTrackerType.EDA_CONTINUOUS as the parameter.
HealthTrackerService
HealthTrackerService initiates a connection to Samsung's Health Tracking Service and provides an HealthTracker instance to track a HealthTrackerType.
|
|
HealthTracker
|
getHealthTracker(HealthTrackerType healthTrackerType)
Provide a HealthTracker instance for the given healthTrackerType.
|
/****************************************************************************
* [Practice 2] Setup EDA tracker
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* Use the provided variable 'edaTracker' which is currently null.
* Initialize EDA Tracker with proper Sensor SDK functionality.
* Call getHealthTracker() function on 'healthTrackingService' object.
* As an argument use HealthTrackerType.EDA_CONTINUOUS.
* Assign the obtained tracker to 'edaTracker' variable.
****************************************************************************/
fun obtainEDATracker(): HealthTracker? {
var edaTracker: HealthTracker? = null
// TODO: Assign the tracker to the 'edaTracker' variable here
return edaTracker
}
Start and stop the tracker
For the client app to begin retrieving data through the SDK, set a listener method on the HealthTracker. If successful, the event listener collects the sensor data until the measurement is stopped in the app.
NoteOnly one HealthTracker.TrackerEventListener should be set per HealthTrackerType.
HealthTracker
HealthTracker enables an application to set an event listener and receive the Galaxy Watch's sensor data for a specific HealthTrackerType.
|
|
| void
|
setEventListener(HealthTracker.TrackerEventListener listener)
Set an event listener for this HealthTracker instance.
|
fun startTracking() {
edaTracker = obtainEDATracker()
if (edaTracker != null) {
edaTracker!!.setEventListener(trackerListener)
_progressState.value = ProgressState.Measuring(true)
} else {
scope.launch {
_messageState.emit(MessageState.TrackerNotInitialized)
}
}
}
To stop the measurement, unset the TrackerEventListener from the HealthTracker object.
HealthTracker
HealthTracker enables an application to set an event listener and receive the Galaxy Watch's sensor data for a specific HealthTrackerType.
|
|
| void
|
unsetEventListener()
Stop the registered event listener for this HealthTracker instance.
|
fun stopTracking() {
if (edaTracker != null) {
edaTracker!!.unsetEventListener()
_progressState.value = ProgressState.Measuring(false)
}
}
Obtain EDA data
The EDA values are provided in the onDataReceived callback of TrackerEventListener at a frequency of 1Hz. The platform's response is asynchronous and includes a data point object containing all the required information.
In the EDATrackingManager.kt file, navigate to extractEdaValues() function.
To obtain EDA data, read the skin conductance value and measurement status. This can be extracted by specifying the appropriate keys in the getValue() function from the DataPoint. Additionally, obtain the timestamp of the incoming data by calling the getTimestamp() function from the DataPoint.
- Retrieve the skin conductance value using the
getValue() function with the key ValueKey.EdaSet.SKIN_CONDUCTANCE.
- Retrieve the measurement status using the
getValue() function with the key ValueKey.EdaSet.STATUS.
- Obtain the timestamp of the incoming data using the
getTimestamp() function.
DataPoint
DataPoint is a map of ValueKey and value with a timestamp.
|
|
| long
|
getTimestamp()
Get a timestamp of the DataPoint.
|
<T> T
|
getValue(ValueKey<T> type)
Get a data value for the given key.
|
/****************************************************************************
* [Practice 3] Read values from DataPoint object
* - Get skin conductance value
* - Get status value
* - Get timestamp
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* Use the provided variable 'skinConductance' which is currently null.
* Obtain skin conductance value using dataPoint.getValue(ValueKey.EdaSet.SKIN_CONDUCTANCE).
* Assign the obtained value into 'skinConductance' variable.
*
* Use the provided variable 'edaStatus' which is currently null.
* Obtain status using dataPoint.getValue(ValueKey.EdaSet.STATUS).
* Assign the obtained value into 'edaStatus' variable.
*
* Use the provided variable 'edaTimestamp' which is currently null.
* Obtain the 'timestamp' property from 'dataPoint' object.
* Assign the obtained value into 'edaTimestamp' variable.
****************************************************************************/
fun extractEdaValues(dataPoint: DataPoint): EDAValue {
var skinConductance: Float? = null
var edaStatus: Int? = null
var edaTimestamp: Long? = null
// TODO: Assign the SKIN_CONDUCTANCE value to the 'skinConductance' variable here
// TODO: Assign the STATUS value to the 'edaStatus' variable here
// TODO: Assign the timestamp property to the 'edaTimestamp' variable here
return EDAValue(skinConductance, EDAStatus.fromInt(edaStatus), edaTimestamp)
}
Run unit tests
For your convenience, you can find an additional Unit Tests package. This lets you verify your code changes even without using a physical watch. See the instructions below on how to run the unit tests:
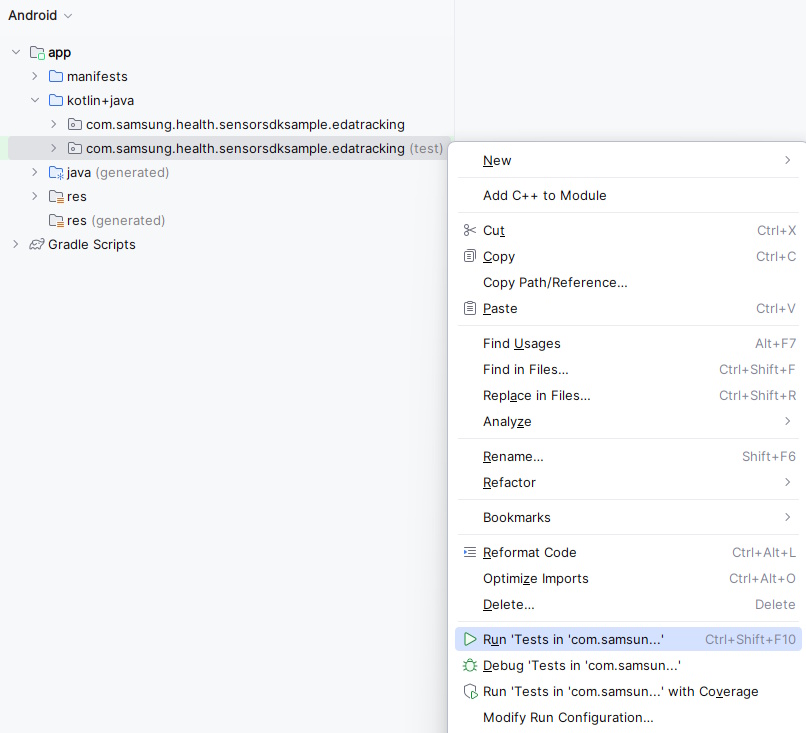
- Right-click on com.samsung.health.sensorsdksample.edatracking (test) and select Run ‘Tests in ‘com.samsung.health.sensorsdksample.edatracking’’.
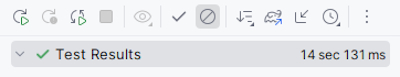
- If you completed all the tasks correctly, you can see that all the unit tests passed successfully.
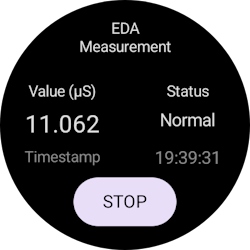
Run the app
After building the APK, you can run the application on a connected device to measure your electrodermal activity values.
- Once the application starts, grant the app permission to access your vital signs information.

- Tap the Start button to begin the Electrodermal Activity measurement. The app shows your skin conductance, measurement status, and the time of the recorded data.
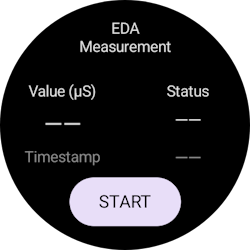
- Tap the Stop button to stop the measurement.
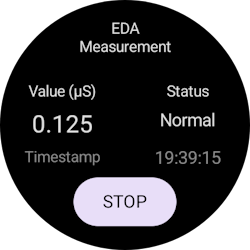
You're done!
Congratulations! You have successfully achieved the goal of this Code Lab. Now, you can create a health app that measures Electrodermal Activity (EDA) on your own! If you are having trouble, you may download this file:
Electrodermal Activity Complete Code (159.3 KB)
To learn more about Samsung Health, visit:
developer.samsung.com/health








