Samsung IAP Publish API Web Integration
Md. Hossain
Engineer, Samsung Developer Program
Introduction
The Samsung IAP Publish API enables developers to efficiently manage in-app purchase (IAP) products within applications. This API serves as the foundation for handling CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations related to digital products available for purchase. Developers can use this API to view existing in-app products, register new products, modify product details such as price and description, and remove products that are no longer needed.
As a part of this article, we will develop a backend application server and a web application to streamline Samsung IAP product management. The backend server will communicate with the Samsung server through the Samsung IAP Publish API, handling requests related to IAP products to ensure smooth integration and operation. The web application will provide an intuitive, user-friendly interface, allowing developers and administrators to visually manage Samsung IAP products in a structured and organized manner.
By implementing this system, developers can significantly reduce manual effort while maintaining better control over their IAP products. Additionally, the Publish API enables a unified product backend, helping standardize workflows, enforce consistent policies, and maintain clear audit trails—further enhancing the design and operational efficiency of IAP management.
To begin, you need to have a mobile application in Galaxy Store so that you can create Samsung IAP products. If you do not have one, follow the Integration of Samsung IAP Services in Android Apps article.
API overview
The Samsung IAP Publish API allows developers to manage IAP products in their applications by viewing, creating, updating, modifying, and deleting products.
Base URL
The base URL for accessing the Samsung IAP Publish API endpoints is.
https://devapi.samsungapps.com/iap/v6/applications/:packageName/items
Replace packageName with the actual package name of your application to access the relevant Samsung IAP endpoints.
Supported method
The Samsung IAP Publish API allows fetching a list of available products or viewing detailed information about a specific product using GET requests. To register a new product, developers can send a POST request, while updating an existing product requires a PUT request. If only partial modifications are needed, a PATCH request is needed. Finally, products can be removed with a DELETE request.
Header
Add the following fields to the request header.
- Authorization: This field requires Bearer token which is the access token from Galaxy Store authentication server. For more information, see the Create an Access Token page.
- Service Account ID: Get the Service Account ID value by clicking the Assistance > API Service tabs on the Seller Portal. For more details, read the section Create a service account and follow step 6.
- Content-Type: Use
application/jsonas value.
Implementation of Samsung Publish API
The Samsung IAP Publish API helps to manage IAP products by performing CRUD operations such as viewing, creating, updating, and removing products. To use these operations, we need to set up a server that processes API requests and executes these operations as instructed.
First, create a server. Once the server is ready, we can integrate the Samsung API for server-to-server communication.
In this example, we use OkHttp for network communication to call the API. The front-end communicates with the Spring Boot server, and the Spring Boot server, in turn, interacts with the Samsung IAP service.
Implementation of the "Create Product" operation
A POST request is needed to create a new product. For more details, refer to the documentation.
private static final String CREATE_API_URL = "https://devapi.samsungapps.com/iap/v6/applications/com.example.bookspot/items";
@PostMapping(value = "/create", consumes = org.springframework.http.MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ResponseEntity<String> createItem(@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody String requestBody) {
okhttp3.MediaType mediaType = okhttp3.MediaType.parse("application/json");
okhttp3.RequestBody body = okhttp3.RequestBody.create(mediaType, requestBody);
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(CREATE_API_URL)
.post(body)
.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + ACCESS_TOKEN)
.addHeader("service-account-id", SERVICE_ACCOUNT_ID)
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
String responseString = response.body() != null ? response.body().string() : "No response body";
return ResponseEntity.status(response.code()).body(responseString);
} catch (IOException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(500).body("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
Example response
After successful execution of the POST request, the server will respond with the status 200 (Success). Below is the visual representation of the operation.

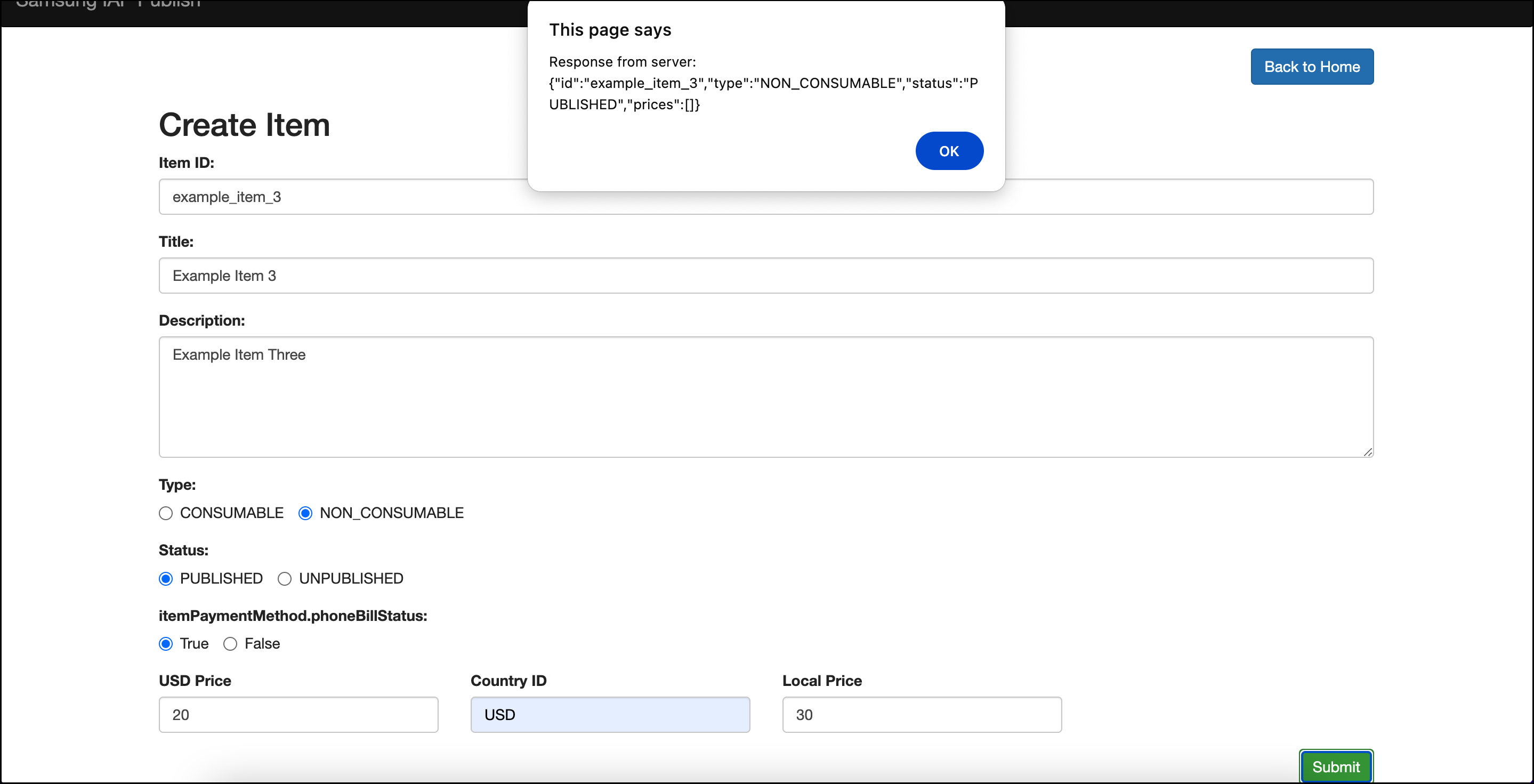


Figure 1: UI representation of Create Product operation

For a list of possible response codes when a request fails, refer to Failure response codes.
Implementation of the "View Product List" operation
To view the already created products, we need to fetch them from the Samsung server. For this, we need to build a GET request to retrieve the products. For more details, refer to the documentation.
private static final String VIEW_API_URL = "https://devapi.samsungapps.com/iap/v6/applications/com.example.bookspot/items?page=1&size=20";
@GetMapping("/get")
public ResponseEntity<String> getRequest() {
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(VIEW_API_URL)
.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + ACCESS_TOKEN)
.addHeader("service-account-id", SERVICE_ACCOUNT_ID)
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (!response.isSuccessful()) {
String error = response.body() != null ? response.body().string() : "Unknown error";
return ResponseEntity.status(response.code()).body("Failed: " + error);
}
String json = response.body() != null ? response.body().string() : "{}";
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.contentType(org.springframework.http.MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.body(json);
} catch (IOException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(500).body("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
Example response
After the request is successfully sent to the server, it will respond with the status code 200. Below is the visual representation of the product retrieval process.

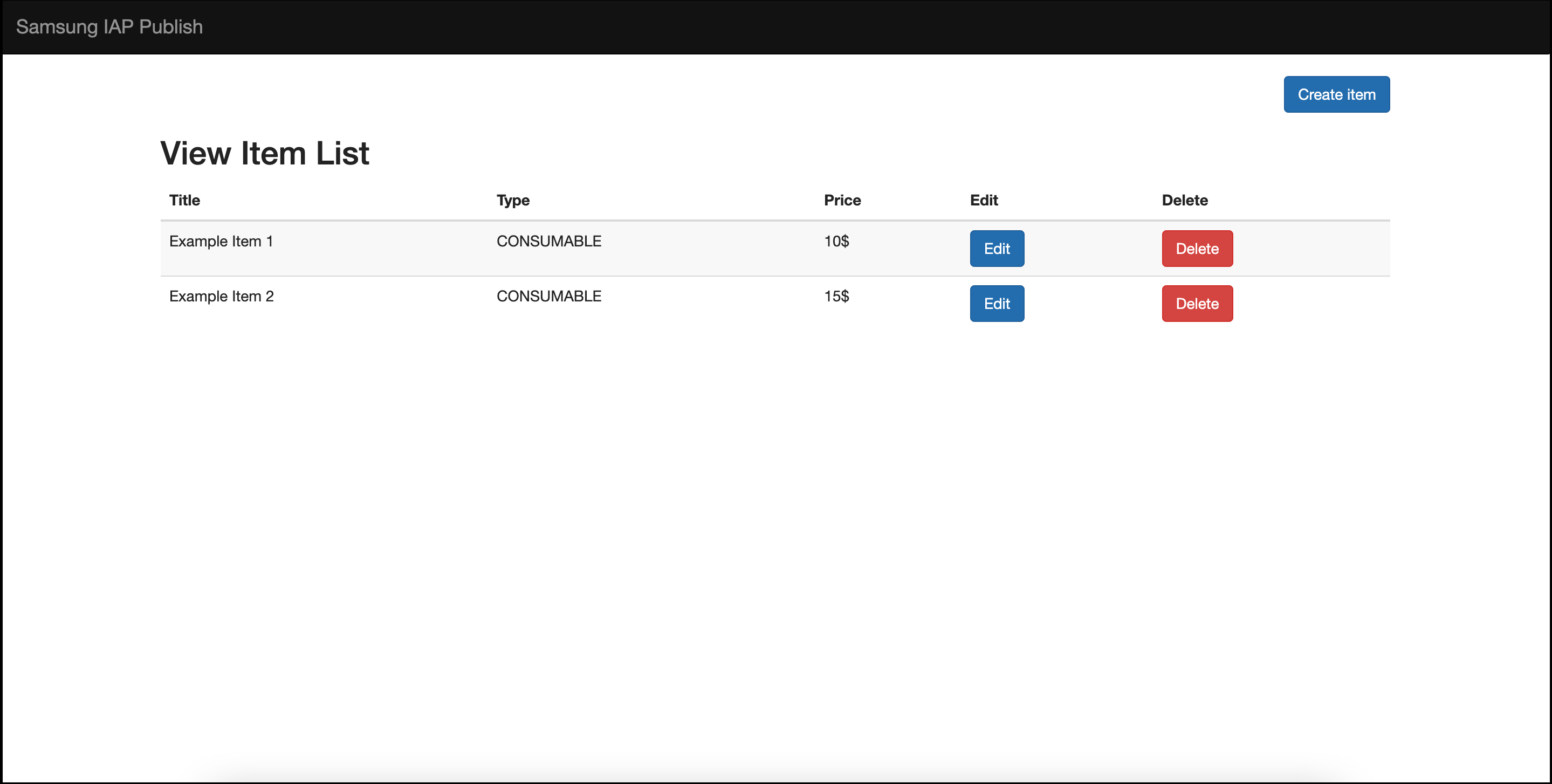


Figure 2: UI representation of View Product List operation

For a list of possible response codes when a request fails, refer to Failure response codes.
Implementation of the "Modify Product" operation
To modify the listed products, we need to create a PUT request based on the required fields and perform the modification operation accordingly. For more details, refer to the documentation.
private static final String MODIFY_API_URL = "https://devapi.samsungapps.com/iap/v6/applications/com.example.bookspot/items";
@PutMapping(value = "/update", consumes = org.springframework.http.MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ResponseEntity<String> updateItem(@RequestBody String requestBody) {
okhttp3.MediaType mediaType = okhttp3.MediaType.parse("application/json");
okhttp3.RequestBody body = okhttp3.RequestBody.create(mediaType, requestBody);
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(MODIFY_API_URL)
.put(body)
.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + ACCESS_TOKEN)
.addHeader("service-account-id", SERVICE_ACCOUNT_ID)
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
String responseString = response.body() != null ? response.body().string() : "No response body";
return ResponseEntity.status(response.code()).body(responseString);
} catch (IOException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(500).body("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
Example response
Below is a visual representation of a response to a successful modification request.

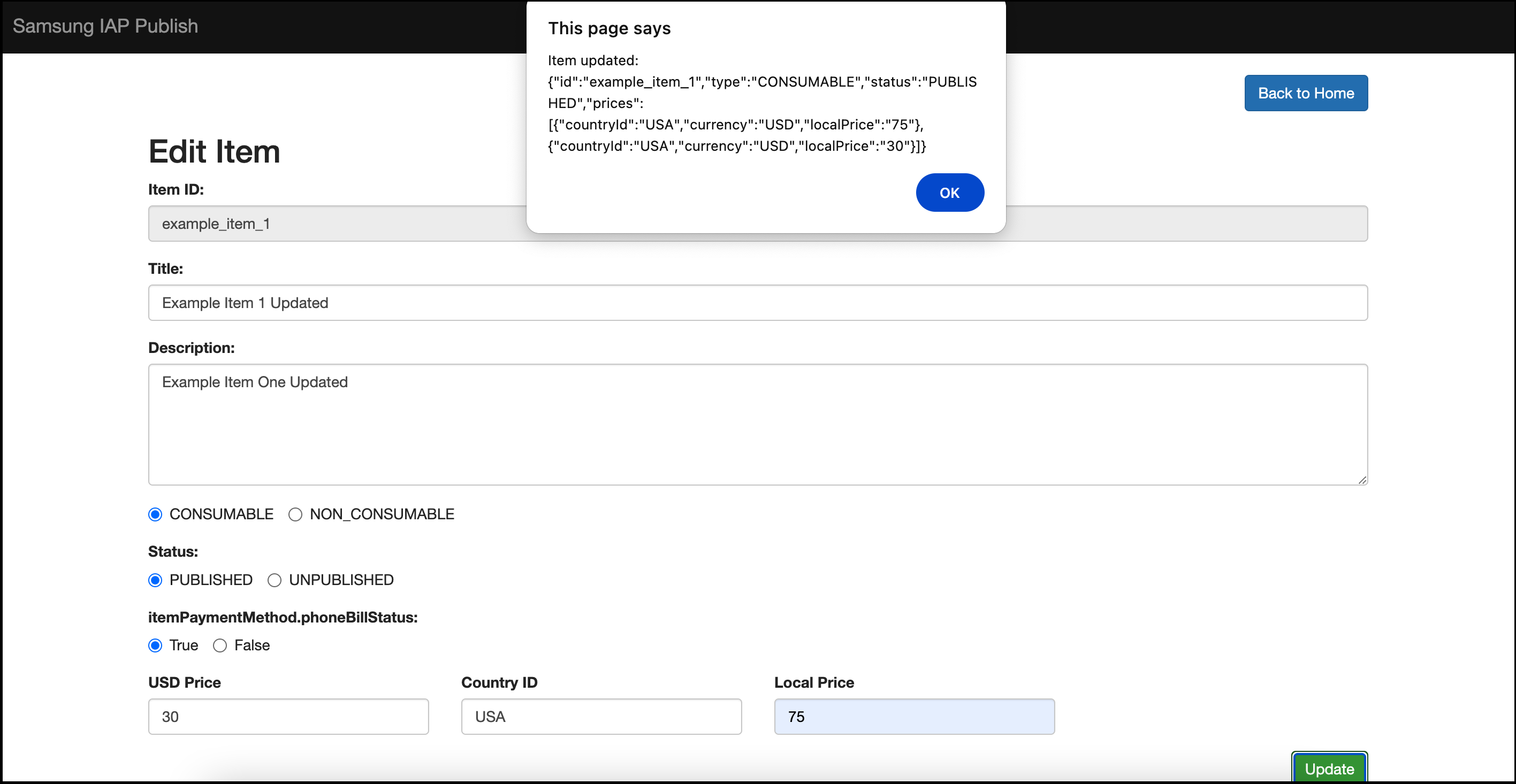


Figure 3: UI representation of Modify Product operation

For a list of possible response codes when a request fails, refer to Failure response codes.
Implementation of the "Remove Product" operation
To delete a product from the server, we need to make a DELETE request using the necessary fields and execute the item removal operation accordingly. For more details, refer to the documentation.
private static final String REMOVE_API_URL = "https://devapi.samsungapps.com/iap/v6/applications/com.example.bookspot/items";
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{itemId}")
public ResponseEntity<String> deleteItem(@PathVariable String itemId) {
String deleteUrl = REMOVE_API_URL + "/" + itemId;
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(deleteUrl)
.delete()
.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + ACCESS_TOKEN)
.addHeader("service-account-id", SERVICE_ACCOUNT_ID)
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
String responseString = response.body() != null ? response.body().string() : "No response body";
return ResponseEntity.status(response.code()).body(responseString);
} catch (IOException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(500).body("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
Example response
Below is a visual representation of the item retrieval process after a successful remove operation.

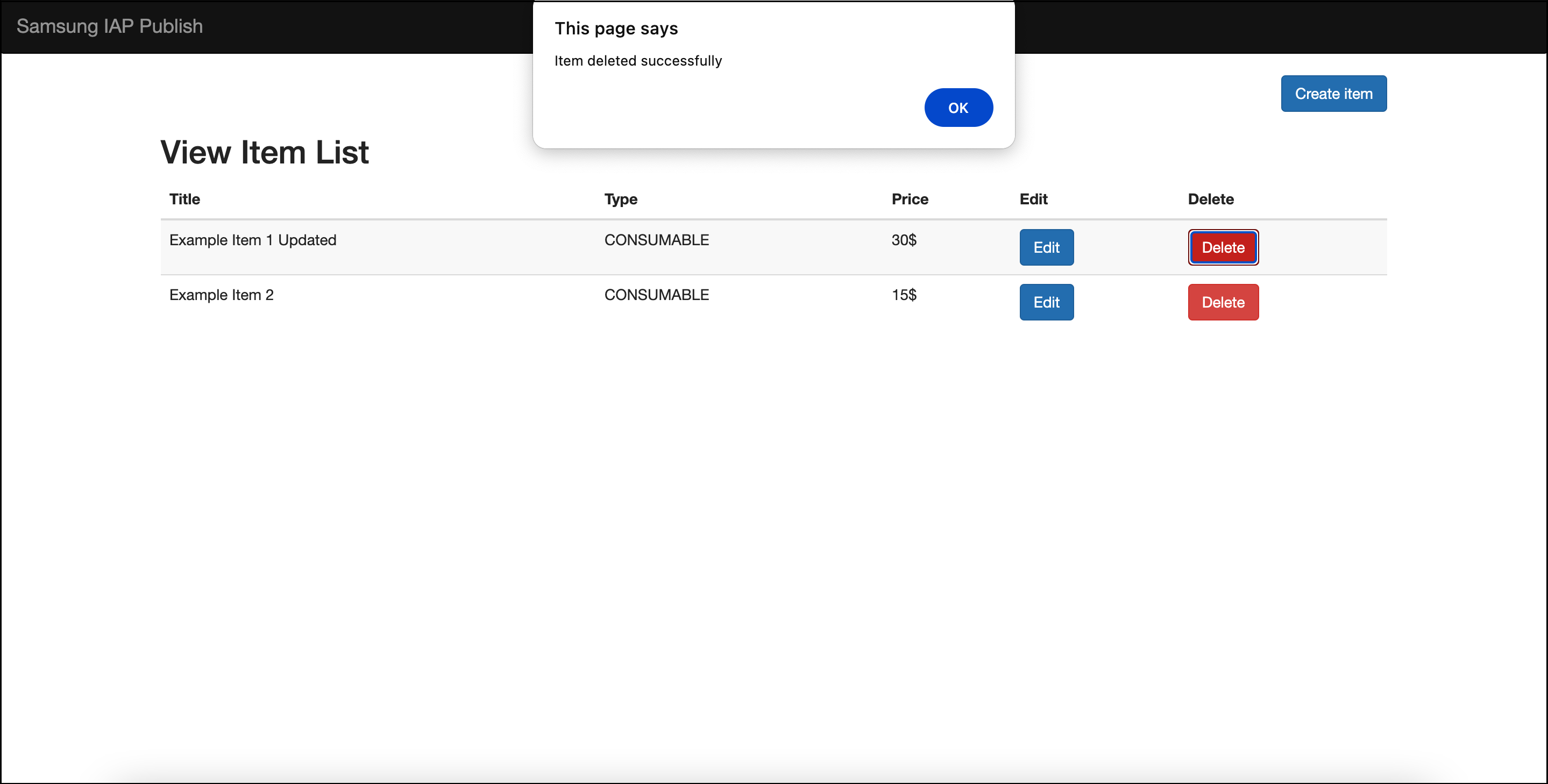


Figure 4: UI representation of Delete Product operation

For a list of possible response codes when a request fails, refer to Failure response codes.
Deploy the server
You can deploy your server to CodeSandbox for testing purposes. You also can use any other hosting site according to your requirements.
Conclusion
By effectively incorporating the Samsung IAP Publish API, you can create your own webview to easily manage your IAP products.
References
For additional information on this topic, refer to the resources.


